Glory Tips About How To Tell If You Are Bow Legged
Bowleggedness is a condition very common in toddlers.
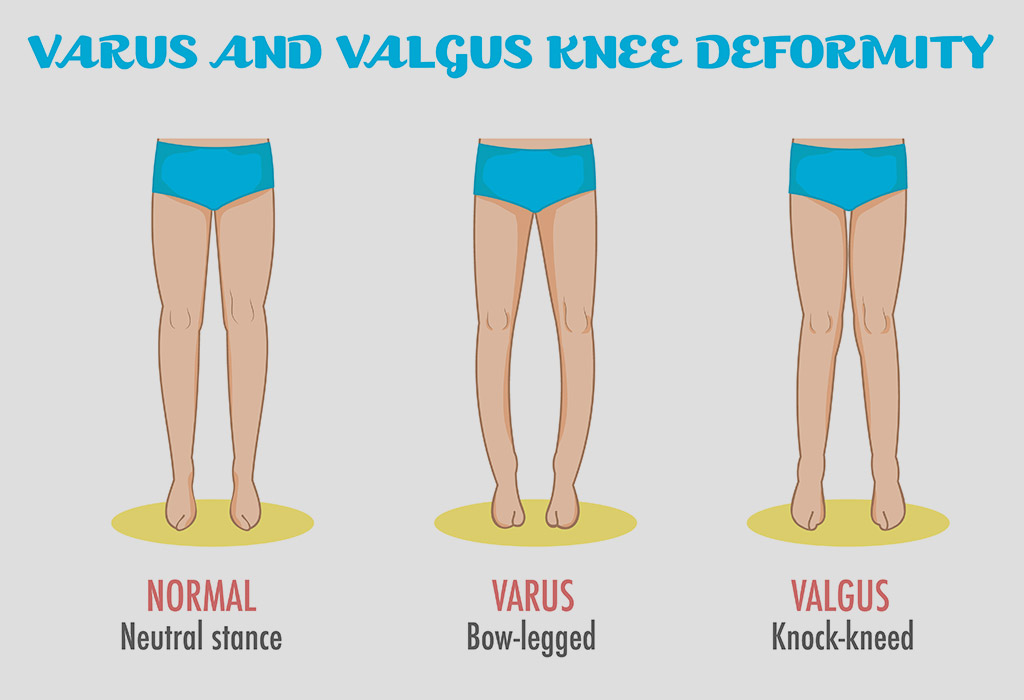
How to tell if you are bow legged. Other symptoms experienced by people with bowlegs. Bow legs (genu varum) is a condition where one or both of your child’s legs curve outward at the knees. This creates a wider space than normal between the knees and lower legs.
Find out how to tell if your child is bowlegged. Knock knees are when the legs curve in at the knees. Balance exercise for bow legs.
Advertisement advertisement learn why your child's legs might appear curved and whether bowlegs are a cause for concern. The most common symptom of a bowleg condition is that a person's knees do not touch while standing with their feet and ankles together. Bowlegs are legs that curve outward at the knee, keeping the knees apart even when the ankles are together.
The bowing is asymmetric (the legs are bowed to different degrees). This causes a bowing of the legs that, if it continues beyond three years of age, suggests there is a bowleg deformity. Foot and nail care.
Both bow legs and knock knees happen when the bones. Look for symptoms like outwardly curved legs, intoeing, or an awkward walk. After washing your child's feet, dry them well between the toes.
You know you may have bowed legs and varus knees if you can fit a fisted hand between your knees while standing uprigh The definitive sign of bow legs is the “bowing” or outward curving of the knees when the child stands with the ankles together. When cutting their toenails, cut straight across, otherwise they may get an ingrown toenail.
To understand bowlegs, also called genu varum, it is important to. Be aware of pathological causes such as rickets and blount ’s. Find out how to tell if your child is bowlegged.
Hand fits thru knees: Bow legs is a condition in which a person’s legs appear to bow or bend outward. Bow legs are when the legs curve out at the knees.
Physiologic bowing is the most common cause of bow legs and is seen from birth until two or three years of age. There is typically a gap between the lower legs and. The child has symptoms such as pain, limping, weakness, or trouble running.